Lewis Electron Dot Structure of Sulfur Trioxide SO3 & Electrostatic Potentials ESP
A simple procedure for writing Lewis Structures was given in a previous article entitled “Lewis Structures and the Octet Rule”. Several worked examples relevant to this procedure were given in previous posts please see the Sitemap - Table of Contents (Lewis Electron Dot Structures).
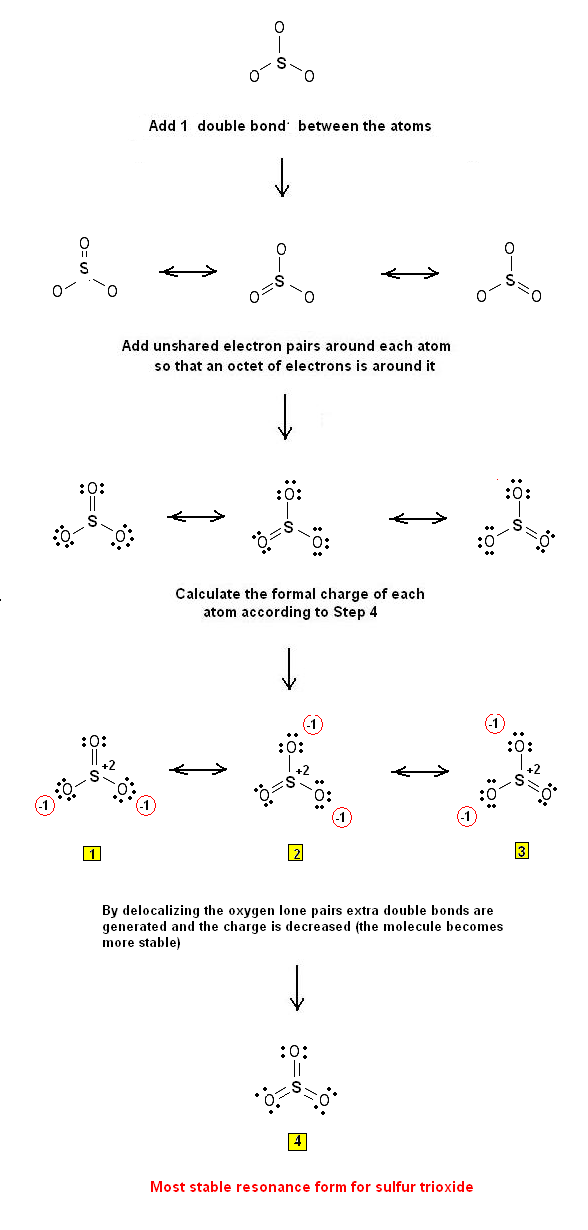
The Lewis Electron Dot Structures of SO3 were drawn using this procedure in a previous article entitled "Simple Procedure for writing Lewis Structures – Lewis Structures for sulfur trioxide SO3"
Lewis structures #1 - #4 are the derived resonance structures:
Molecular Orbital Theory and ab initio calculations can be used to calculate and draw the electrostatic potential (ESP) of a molecule.
The molecular electrostatic potential is the potential energy of a proton at a particular location near a molecule. There are negative and positive ESP's.
Negative electrostatic potential corresponds to a attraction of the proton by the concentrated electron density in the molecules (mainly from lone pairs, pi-bonds,... ) (colored red). Red color in electrostatic potential drawings show areas with high electron density.
Positive electrostatic potential corresponds to repulsion of the proton by the atomic nuclei in regions where low electron density exists and the nuclear charge is incompletely shielded (colored blue). Blue color in electrostatic potential drawings show areas with low electron density.
Several ab initio softwares calculate electrostatic potentials based on quantum mechanically derived molecular orbitals. The electrostatic potential of SO3 derived by ab initio calculations is shown below:
It is to be noted that most of the negative charge (electron rich areas, colored red) is concentrated on the oxygen atoms of SO3 as it is expected from the Lewis structures of SO3 and by chemical intuition. Most of the positive charge (electron deficient areas, colored blue) is concentrated on the S atom as it is expected from the Lewis structures of SO3 and by chemical intuition.
Relevant Posts
Lewis Structures|Octet Rule: A Simple Method to write Lewis Structures
Lewis structure of SO2 – Simple Procedure for drawing Dot structures
Lewis Dot Structure of the sulfite ion SO3-2
References
- G.N. Lewis, J.A.C.S, 38, 762-785, (1916)
- E. C. McGoran, J. Chem. Educ., 68, 19-23 (1991)
- A.B.P. Lever, J. Chem. Educ., 49, 819-821, (1972)
Key Terms
resonance structures of sulfur trioxide SO3, Lewis electron structures of SO3, chemical formula of SO3, simple method for drawing Lewis structures of SO3, electrostatic potential, ab initio,molecular orbital theory
u>

No comments:
Post a Comment