A simple procedure for writing Lewis structures is given in a previous article entitled “Lewis Structures and the Octet Rule”. Relevant worked examples were given in the following articles: Examples #1, #2, #3 , #4, #5, #6, #7, #8, #9, #10, #11, #12 and #13.
Another example for writing Lewis structures following the above procedure is given bellow:
Step 3 & 4:
The Lewis structures for C3H4 are as follows:
Another example for writing Lewis structures following the above procedure is given bellow:
Let us consider the case of
allene (C3H4). Allenes have proven themselves to
be valuable building blocks toward complex molecular targets, revealing novel
applications in natural product synthesis, pharmaceutical chemistry and
material science. The ongoing interest in allene chemistry results in a variety
of new methodologies and pathways for the synthesis of allenes.
Step 1: Connect the atoms with single bonds
Step 2: Calculate the # of electrons in π bonds (multiple bonds) using formula (1) in the article entitled “Lewis Structures and the Octet Rule”.:
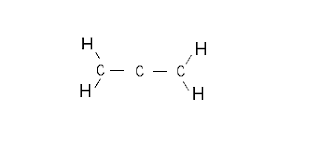 |
| Fig. 1: Connecting the allene atoms with single bonds (step 1) |
Where n in this case is 3
(exclude the H atoms)
Where V = (4 + 2 + 4 + 4+ 2) = 16
Therefore, P = 6n + 2 – V = 6 * 3
+ 2 – 16 = 4 So there are 4 π electrons in C3H4 . Therefore, 2 double bonds or 1 triple bond must be added to the structure of Step
1.
 |
| Fig. 2: Lewis electron dot structure for the allene molecule C3H4 |
please how can you use your formula to write Lewis' structure for NH4+(ammonium)
ReplyDelete